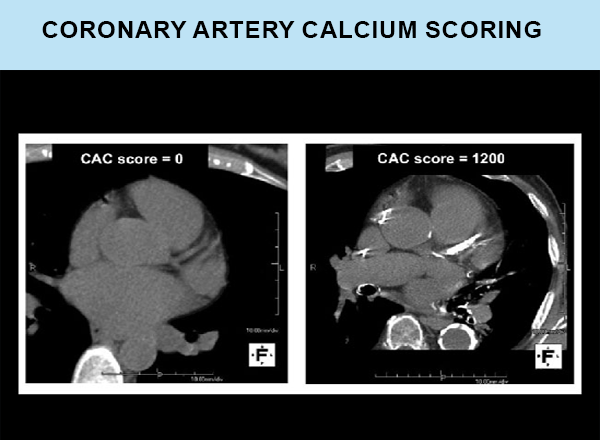
CT Coronary Artery Calcium Scoring
The coronary arteries are the vessels that supply blood to the heart. Plaque or calcium build-up in the coronary arteries causes heart disease or can lead to a heart attack. A test called Coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring can detect this build up and is a good predictor of coronary events. This test has been demonstrated to be a better predictor than cholesterol levels in medical studies.
This is done using special X Ray equipment called a CT scanner which takes pictures of the blood vessels supplying the heart. The entire procedure is usually completed with in about 10 Minutes.
How is a CAC score calculated?
A calcium score (sometimes called an Agatston score) is calculated based on the amount of plaque observed in the CT scan.
What is the significance of the CAC score?
Based on your score, your doctor will be able to do risk stratification and suggest preventive strategies or further evaluation.
- Zero: No plaque. Your risk of heart attack is low.
- 1 – 10: Small amount of plaque. You have less than a 10 percent chance of having heart disease, and your risk of heart attack is low.
- 11-100: Some plaque. You have mild heart disease and a moderate chance of heart attack. Your doctor may recommend other treatment in addition to lifestyle changes.
- 101 – 400: Moderate amount of plaque. Your chance of having a heart attack is moderate to high.
- Over 400: Large amount of plaque. This signifies that there is extensive deposition of calcium in the arteries. Your chance of heart attack is high and aggressive prevention strategies are to be used.